Useful Life In Machinery Appraisal
- Erhan Saraç

- Jul 7, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Jan 28, 2025
The purpose of the assessment is to determine, in general terms, the financial state of the business and its operational outcome in the most realistic way and to analyze current market conditions along with the appreciated value, economic and technological changes. The purpose of the evaluation is determined prior to the evaluation process, thus determining other stages of the evaluation process and the evaluation approaches to use.
The concept of ‘‘depreciation’‘ is important in the way cost approximation is commonly used in the valuation of one of the methods of valuation, industrial facilities, and all assets that do not have a second-hand market. Besides immoveable assets, business assets such as machine-equipment, auxiliary equipment, vehicle vehicles, fixtures, and so on are gradually losing value.
The concept of depreciation refers to the systematic and rational cost-reflection of the effect of the depreciation of assets after their acquisition costs and the depreciation of the residual value as stated by International Standards. Useful life refers to the average year in which an asset is considered available before it is depreciated. Financially, it also means the time when an asset can provide an economic benefit for the business.
When performing cost-effective (useful) life analyzes, only the overall lifecycle of that asset group under market conditions should be considered, as well as the factors such as the frequency of use in the business, how often requiring maintenance-repair in the relevant asset specification and limited-time use rights. Thus, the financial reporting studies and the determination of the lifetime of each asset group under the International Assessment Standards have been left to the assessor’s discretion, with the general use in mind and support for the assigned viewpoint with analysis.
There are also significant factors that could affect the valuation result, as well as the revaluation of material assets and the assigning of services from professionals who are able to perform the above-mentioned analysis of the economic life and remaining economic life of assets in the context of PPA studies.
Examples of economic lifetimes accepted throughout the market on the basis of power plants can be specified as follows; Wind Power Plant 25 year, Solar Power Plant 25 year, Hydroelectric Power Plant 50 year and Biomass Power Plant 30 year.
For mono crystal panels, which are among the most preferred solar panels, economic life is considered an average of 25 years. Although there are different linear performance guarantees granted by manufacturers over the economic lifetime, the annual yield loss averages from 0.7% to 0.8%.
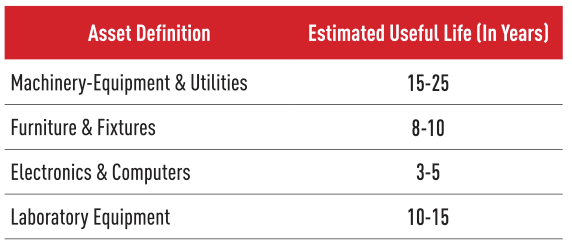
The economic life expectancy for wind turbines is estimated to be in the range of 25-30 years, but due to static charges for the turbine blades, their life cycle will be in the range of 20-25 years. Examples of an entity group can be given as follows



Comments